SiouxFalls - (Parametric) Price of Anarchy¶
1. Imports and data readin¶
First we load the paminco package and read the SiouxFalls data.
The data was taken from here and converted to our format of choice: XML.
The data for SiouxFalls comes with paminco and can be easily loaded:
import paminco
sioux = paminco.load_sioux()
By default the edge cost equal the link travel time: \(F_e = l_e\). The link travel time is defined as
2. Fixed Price of Anarchy with Frank-Wolfe¶
We find minimum cost flows that coincide with user equilibrium and system optimum if we transform the edge cost by:
import copy
# Calculate user equilibrium -> F_e = integral_0^(x_e) l_e(s)ds
sioux_ue = copy.deepcopy(sioux)
sioux_ue.cost.integrate(inplace=True)
fw_ue = paminco.NetworkFW(sioux_ue)
fw_ue.run(max_iter=500)
# Calculate system optimum -> F_e = x_e * l_e
sioux_so = copy.deepcopy(sioux)
sioux_so.cost.times_x(inplace=True)
fw_so = paminco.NetworkFW(sioux_so)
fw_so.run(max_iter=500)
The Price of Annarchy (PoA) measures the inefficency of the network utilization due to selfish behaviour of the participants. It is calculated as the ratio of the total (or equivalently average) travel time for all particpants in the user equilbrium to that of the system optimum:
where \(C\) is the total system travel time (TSTT):
i.e., the objective function of the system optimal minimum cost flow.
def TTST(x):
return (x * sioux.cost(x)).sum()
The Price of Anarchy for SiouxFalls is about 3.8 percent:
poa = TTST(fw_ue.x) / TTST(fw_so.x)
poa
1.0388035657861383
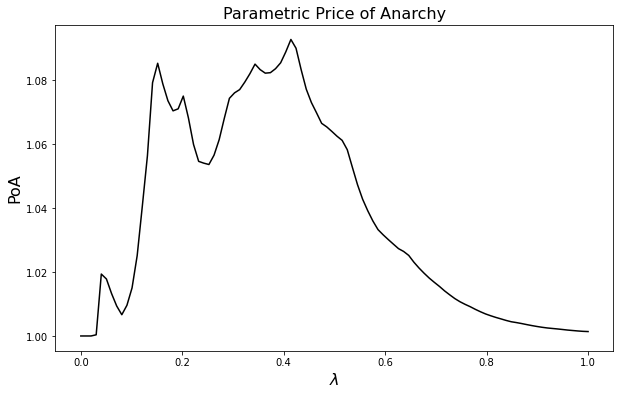
3. Paramtric Price of Anarchy with MCA¶
The above example allowed to compute system inefficiency for a fixed demand \(\mathbf{B}\).
However, it is of interest how the POA varies by the demand multiplier \(\lambda\).
We can achieve this with the MCA algorithm by calculating parametric user equilibira flows and parametric system optima:
sioux2 = copy.deepcopy(sioux)
sioux2.set_demand(("20", "3", 100000))
sioux_ue = copy.deepcopy(sioux2)
sioux_ue.cost.integrate(inplace=True)
mca_ue = paminco.MCA(sioux_ue)
mca_ue.run()
sioux_so = copy.deepcopy(sioux2)
sioux_so.cost.times_x(inplace=True)
mca_so = paminco.MCA(sioux_so)
mca_so.run()
For any demand multiplier in \(\lambda \in [0, 1]\), we can now compute a price of anarchy:
import numpy as np
lambdas = np.linspace(1e-5, 1, 100)
cost_user_equilibira = np.array([TTST(mca_ue.flow_at(l)) for l in lambdas])
cost_system_optima = np.array([TTST(mca_so.flow_at(l)) for l in lambdas])
paramtric_poa = cost_user_equilibira / cost_system_optima
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 6))
ax.plot(lambdas, paramtric_poa, color="black")
ax.set_xlabel("$\lambda$", fontsize=16)
ax.set_ylabel("PoA", fontsize=16)
ax.set_title("Parametric Price of Anarchy", fontsize=16)
Text(0.5, 1.0, 'Parametric Price of Anarchy')